Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy: Complete Guide to Eye Care and Prevention
Introduction
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of vision loss among adults with diabetes. It develops when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing them to leak fluid or bleed. Over time, this can lead to permanent vision impairment if left untreated. Understanding the treatment for diabetic retinopathy and the importance of regular monitoring can save your vision.
Early detection through a diabetic retinopathy exam allows patients to receive timely interventions, reducing the risk of severe complications. With advancements in modern eye care, there are multiple effective treatment options for managing this condition.
Learn more about our comprehensive eye exam services at Lee Vision.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when diabetes damages the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. The disease typically progresses in stages:
-
Mild Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR): Early stage, small blood vessel changes, mild swelling in retinal tissue.
-
Moderate NPDR: More blood vessels become blocked, fluid leakage increases.
-
Severe NPDR: Large areas of the retina lose blood supply, leading to new vessel growth.
-
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR): Advanced stage, new abnormal blood vessels form, increasing the risk of bleeding, retinal detachment, and vision loss.
For detailed information, visit American Diabetes Association.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Symptoms may not appear in the early stages, which is why regular diabetic retinopathy exams are crucial. Common signs include:
-
Blurred or fluctuating vision
-
Seeing floaters or dark spots
-
Difficulty seeing at night
-
Distorted vision or loss of vision in severe cases
-
Sudden vision loss in advanced stages
Many patients remain unaware of the disease until a routine eye exam detects it.
Schedule a diabetic retinopathy exam with our specialists at Lee Vision.
Who is at Risk?
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing diabetic retinopathy:
-
People with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes
-
Those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels
-
Individuals with high blood pressure or high cholesterol
-
Long-term diabetic patients (typically over 10 years)
-
Pregnant women with diabetes
Early detection and lifestyle management play a vital role in reducing risk.
Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatment varies depending on the stage of diabetic retinopathy. Some of the most effective methods include:
1. Laser Therapy (Photocoagulation)
Laser therapy seals leaking blood vessels and prevents the growth of new abnormal vessels. It is most effective in patients with moderate to severe NPDR or early PDR. Laser treatment can prevent further vision loss but cannot restore lost vision.
Choosing the right treatment for diabetic retinopathy is critical to protect your vision.
Learn more from National Eye Institute.
2. Anti-VEGF Injections
These medications are injected into the eye to reduce swelling and inhibit abnormal blood vessel growth. Anti-VEGF therapy is commonly used for diabetic macular edema and PDR. Most patients require a series of injections over several months for optimal results.
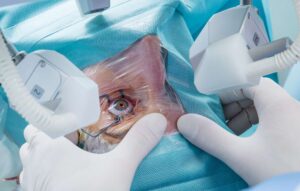
3. Vitrectomy Surgery
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure to remove blood or scar tissue from the vitreous (gel inside the eye). This treatment is typically reserved for advanced PDR when bleeding or retinal detachment occurs.
4. Blood Sugar and Lifestyle Management
Controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining healthy blood pressure, and following a balanced diet can slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol intake are also crucial preventive measures.
Is Diabetic Retinopathy Reversible?
A common question is: “Is diabetic retinopathy reversible?”
-
Early-stage NPDR: Can be slowed or stabilized with proper treatment, blood sugar control, and lifestyle changes.
-
Advanced PDR: Cannot be completely reversed, but treatments like laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and vitrectomy can prevent further vision loss.
-
Lifestyle and medical care: Regular diabetic retinopathy exams, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications improve long-term outcomes.
More insights at Mayo Clinic.
Finding a Diabetic Retinopathy Specialist
Consulting an experienced diabetic retinopathy specialist is essential for proper management. Consider:
-
Board-certified ophthalmologists or retina specialists
-
Clinics offering advanced diagnostic tools and treatment options
-
Personalized care and ongoing monitoring
Contact a trusted diabetic retinopathy specialist at Lee Vision.
Preventing Diabetic Retinopathy
Prevention strategies include:
-
Maintain blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol within recommended levels
-
Regular eye exams (at least annually)
-
Healthy diet rich in antioxidants and low in processed sugar
-
Regular physical activity
-
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
Prevention is always better than treatment, and early detection can save your vision.
Additional Tips for Patients
-
Keep a log of blood sugar readings and share with your doctor
-
Track vision changes and report any sudden changes immediately
-
Use prescribed medications consistently
-
Schedule follow-up eye exams as recommended by your specialist
Book your eye exam today at Lee Vision.
FAQs – Diabetic Retinopathy
Q1: What is the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy?
A1: Treatment depends on the stage. Options include laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, vitrectomy, and strict blood sugar management.
Q2: How often should a diabetic retinopathy exam be done?
A2: Most patients should have an exam at least once a year, or more frequently if advanced disease is present.
Q3: Can diabetic retinopathy be reversed?
A3: Early-stage disease can be stabilized, but advanced diabetic retinopathy cannot be fully reversed.
Q4: How do I find a diabetic retinopathy specialist?
A4: Look for board-certified ophthalmologists or retina specialists experienced in diabetic eye care.
Q5: What are the early symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
A5: Blurred vision, floaters, difficulty seeing at night, and vision changes. Early detection through exams is essential.
Q6: Can lifestyle changes impact diabetic retinopathy?
A6: Yes, controlling blood sugar, maintaining healthy diet and exercise, and avoiding smoking can slow progression.
Conclusion
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy is essential to protect and preserve your vision. Early detection through a diabetic retinopathy exam can prevent severe complications and allow timely intervention. While is diabetic retinopathy reversible depends on the stage of the disease, early management, proper blood sugar control, and regular monitoring can slow progression and maintain healthy eyesight. Consulting an experienced diabetic retinopathy specialist ensures personalized care and access to the latest treatment options, including laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, and vitrectomy when necessary.
Take action today—schedule your eye exam and consult a diabetic retinopathy specialist at Lee Vision to safeguard your vision and maintain optimal eye health.